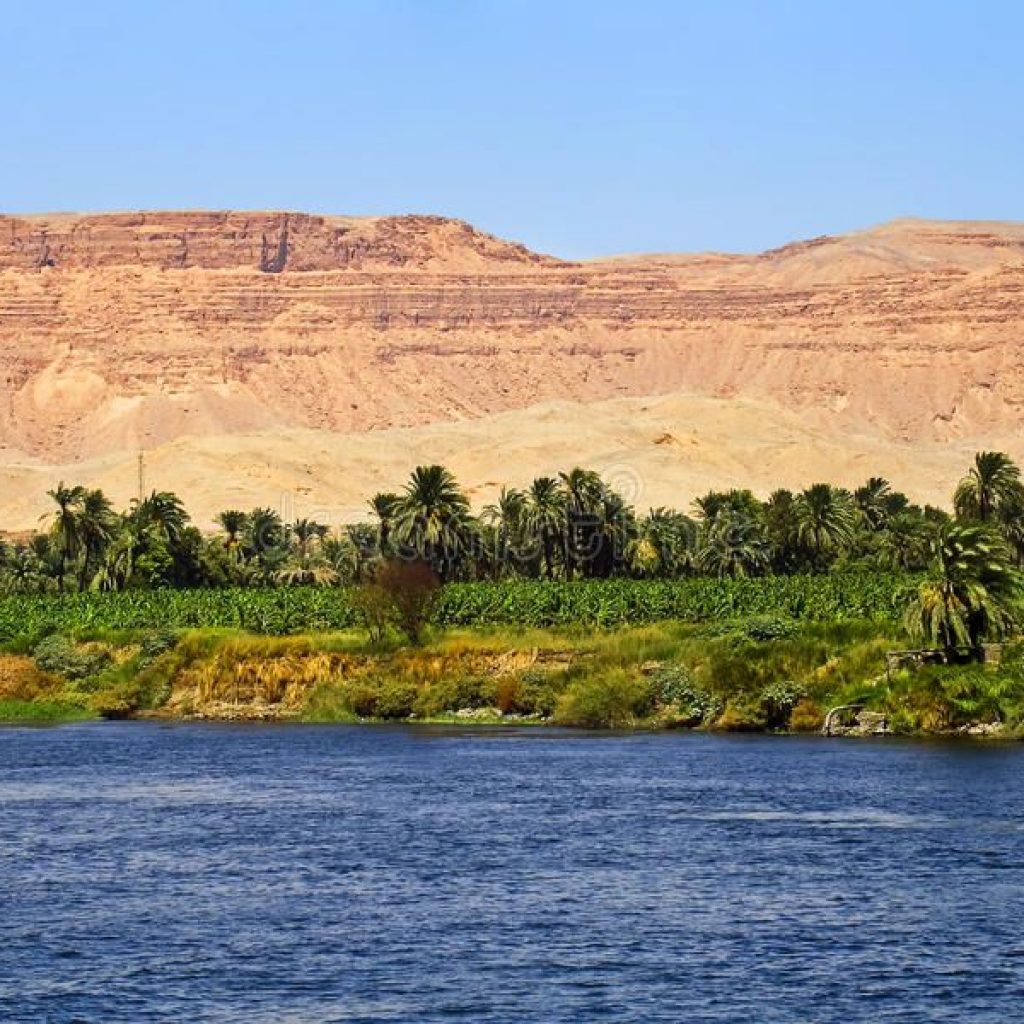
Despite ranking in the top 30 largest countries with its 1 million square kilometers of land, Egypt is a country that is notorious for its geographic ‘distribution.’ 99% of Egypt’s population utilizes only 5% of the total land area but nearly 100% of its aquatic resources as a result of the predominantly barren ecosystem. The lifeline of some 90 million human beings, the river Nile is the focal point of urban planning, an incredible 6,695 km gift of sustenance for Egypt and three other countries, making it the longest, and arguably most vital, river in the world.
The Nile enters Egypt a few kilometers north of a Sudanese town called Wadi Halfa through a narrow canyon that traverses sandstone and granite cliffs. The northward flowing direction of the river has thus earned Egypt’s southern border the name “Upper Egypt.” Within this stretch of the Nile is the world’s most intensive concentration of temples, tombs and palaces constructed over the span of 4,000 years. This includes the temples of Abydos, Dendara, Karnak, Esna, Edfu, Kom Ombo, Philae and Abu Simbel, each conceived for their respective deities, further to the tombs in the Theban Necropolis within the Valley of the Kings across the river from Luxor. Absorbing the river-scape from the comfort of a felucca (small sail boat) is the epitome of pleasure, relished by locals and non-locals alike. This is easily arranged in Aswan, and larger Nile cruise boats can provide an even more luxurious experience. As this river continues to flow upwards past major cities and temples, it begins to branch out into a flower-shaped formation known as the Nile delta, covering 240 km of the Mediterranean coastline. Home to 39 million people, this is Egypt’s most agriculturally rich land with some of the most beautiful, soul-rejuvenating nature Egypt has to offer.




Comment (0)